Introduction
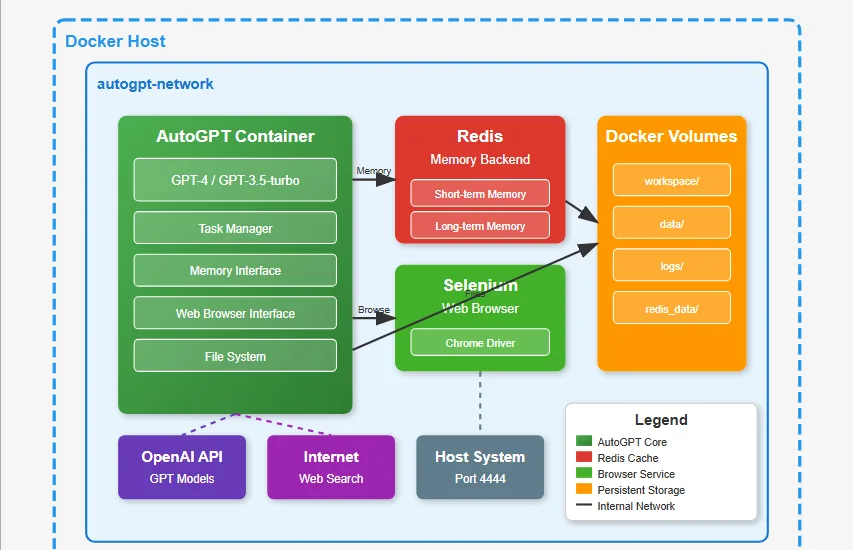
AutoGPT represents a significant advancement in autonomous AI agents, capable of breaking down complex tasks into manageable subtasks and executing them independently. Unlike traditional chatbots that respond to individual prompts, AutoGPT can maintain context across multiple interactions, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specified goals.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through setting up AutoGPT locally using Docker, ensuring a clean, isolated, and reproducible deployment that doesn’t interfere with your host system.
What is AutoGPT?
AutoGPT is an experimental open-source application that demonstrates the capabilities of GPT-4 and GPT-3.5-turbo in autonomous task execution. Key features include:
- Autonomous Operation: Can work independently with minimal human intervention
- Task Decomposition: Breaks complex objectives into smaller, manageable tasks
- Memory Management: Maintains short-term and long-term memory across sessions
- Tool Integration: Can interact with various tools, APIs, and services
- Web Browsing: Capable of searching and extracting information from the internet
- File Operations: Can read, write, and manipulate files
Prerequisites
Before beginning the setup, ensure you have the following:
System Requirements
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows with WSL2
- RAM: Minimum 4GB, recommended 8GB+
- Storage: At least 2GB free space
- Network: Stable internet connection for initial setup and API calls
Required Software
- Docker: Version 20.10 or higher
- Docker Compose: Version 2.0 or higher
- Git: For cloning the repository
API Keys
- OpenAI API Key: Essential for GPT model access
- Optional APIs: Google Search API, ElevenLabs API (for text-to-speech), etc.
Installation Steps
Step 1: Verify Docker Installation
First, confirm Docker is properly installed and running:
docker --version
docker-compose --version
docker run hello-worldIf Docker isn’t installed, follow the official Docker installation guide for your operating system.
Step 2: Clone AutoGPT Repository
Clone the official AutoGPT repository:
git clone https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT.git
cd AutoGPTStep 3: Environment Configuration
Create and configure your environment file:
cp .env.template .envEdit the .env file with your preferred text editor:
nano .envEssential Configuration Parameters:
# OpenAI API Configuration
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key_here
SMART_LLM=gpt-4
FAST_LLM=gpt-3.5-turbo
# Memory Backend (Redis recommended for Docker)
MEMORY_BACKEND=redis
REDIS_HOST=redis
REDIS_PORT=6379
REDIS_PASSWORD=
# Browser Configuration
USE_WEB_BROWSER=seleniumweb
HEADLESS_BROWSER=True
# Security Settings
RESTRICT_TO_WORKSPACE=True
EXECUTE_LOCAL_COMMANDS=False
# Logging
LOG_LEVEL=INFO
LOG_FORMAT=%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)sOptional Advanced Configuration:
# Custom Model Settings
TEMPERATURE=0.7
MAX_TOKENS=4000
# Web Browsing
GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_google_api_key
CUSTOM_SEARCH_ENGINE_ID=your_search_engine_id
# Text-to-Speech
USE_MAC_OS_TTS=False
ELEVENLABS_API_KEY=your_elevenlabs_key
# Plugin System
ALLOWLISTED_PLUGINS=
DENYLISTED_PLUGINS=Step 4: Docker Compose Configuration
AutoGPT includes a pre-configured docker-compose.yml file. Review and customize if needed:
version: '3.8'
services:
auto-gpt:
build: .
env_file:
- .env
volumes:
- ./auto_gpt_workspace:/app/auto_gpt_workspace
- ./data:/app/data
- ./logs:/app/logs
depends_on:
- redis
- selenium
networks:
- autogpt-network
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
command: redis-server --requirepass ${REDIS_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
networks:
- autogpt-network
selenium:
image: selenium/standalone-chrome:latest
ports:
- "4444:4444"
shm_size: 2gb
networks:
- autogpt-network
volumes:
redis_data:
networks:
autogpt-network:
driver: bridgeStep 5: Build and Launch
Build the Docker containers:
docker-compose buildStart AutoGPT:
docker-compose up -dCheck the status of your containers:
docker-compose psConfiguration Deep Dive
Memory Backend Options
AutoGPT supports multiple memory backends:
Redis (Recommended for Docker)
MEMORY_BACKEND=redis
REDIS_HOST=redis
REDIS_PORT=6379Local File System
MEMORY_BACKEND=localPinecone Vector Database
MEMORY_BACKEND=pinecone
PINECONE_API_KEY=your_pinecone_key
PINECONE_ENV=your_pinecone_environmentBrowser Configuration
For web browsing capabilities:
Selenium (Docker-friendly)
USE_WEB_BROWSER=seleniumweb
SELENIUM_WEB_DRIVER_HOST=selenium
SELENIUM_WEB_DRIVER_PORT=4444Chrome/Chromium (Local)
USE_WEB_BROWSER=chrome
HEADLESS_BROWSER=TrueSecurity Considerations
Workspace Restrictions
RESTRICT_TO_WORKSPACE=TrueThis prevents AutoGPT from accessing files outside its designated workspace.
Command Execution
EXECUTE_LOCAL_COMMANDS=FalseDisable local command execution for enhanced security.
AI Model Limits
MAX_TOKENS=4000
TEMPERATURE=0.7Usage Examples
Basic Task Execution
Access the AutoGPT interface:
docker-compose logs auto-gptOr run interactively:
docker-compose run --rm auto-gptExample Task 1: Research Assistant
Goal: Research the latest developments in quantum computing and create a summary report
Example Task 2: Content Creation
Goal: Write a blog post about sustainable energy solutions, including recent statistics and trends
Example Task 3: Data Analysis
Goal: Analyze the CSV file in the workspace and create visualizations of the sales data
Advanced Configuration
Custom Plugin Integration
# Mount custom plugins directory
volumes:
- ./plugins:/app/plugins
- ./auto_gpt_workspace:/app/auto_gpt_workspaceResource Monitoring
# Monitor container resources
docker stats auto-gptTroubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: OpenAI API Rate Limits
Solution: Implement rate limiting and use appropriate model selection
SMART_LLM=gpt-3.5-turbo # Use less expensive model for testing
FAST_LLM=gpt-3.5-turboIssue: Memory Backend Connection Errors
# Check Redis container status
docker-compose logs redis
# Restart Redis if needed
docker-compose restart redisIssue: Selenium Browser Errors
# Check Selenium container
docker-compose logs selenium
# Increase shared memory if needed
services:
selenium:
shm_size: 4gbIssue: Workspace Permission Errors
# Fix workspace permissions
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER ./auto_gpt_workspace
chmod -R 755 ./auto_gpt_workspacePerformance Optimization
Resource Allocation
services:
auto-gpt:
deploy:
resources:
limits:
memory: 2G
cpus: '1.0'
reservations:
memory: 1G
cpus: '0.5'Logging Configuration
LOG_LEVEL=WARNING # Reduce log verbosity in production
LOG_FORMAT=%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)sBest Practices
Security Best Practices
- API Key Management: Never commit API keys to version control
- Network Isolation: Use Docker networks to isolate services
- Workspace Restrictions: Always enable workspace restrictions
- Regular Updates: Keep Docker images and AutoGPT updated
- Monitoring: Implement logging and monitoring for production use
Performance Best Practices
- Resource Limits: Set appropriate CPU and memory limits
- Model Selection: Use cost-effective models for testing
- Caching: Leverage Redis for efficient memory management
- Cleanup: Regularly clean up old containers and images
Development Best Practices
- Version Control: Use specific image tags instead of ‘latest’
- Environment Separation: Use different configurations for dev/prod
- Backup Strategy: Implement regular backups of workspace and data
- Testing: Test configurations in isolated environments first
Advanced Deployment Options
Production Deployment
For production environments, consider:
Docker Swarm Configuration
version: '3.8'
services:
auto-gpt:
image: autogpt:production
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 1
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failureKubernetes Deployment
Version: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: autogpt
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: autogpt
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: autogpt
spec:
containers:
- name: autogpt
image: autogpt:latest
env:
- name: OPENAI_API_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: autogpt-secrets
key: openai-api-keyMonitoring and Observability
Docker Healthchecks
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=10s --start-period=60s --retries=3 \
CMD curl -f http://localhost:8000/health || exit 1Logging with ELK Stack
services:
auto-gpt:
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "10m"
max-file: "3"Maintenance and Updates
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Update AutoGPT
git pull origin main
docker-compose build --no-cache
docker-compose up -dClean Up Resources
# Remove unused containers
docker container prune
# Remove unused images
docker image prune
# Remove unused volumes
docker volume pruneBackup Data
# Backup workspace
tar -czf autogpt-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz auto_gpt_workspace/
# Backup Redis data
docker-compose exec redis redis-cli --rdb /data/backup.rdbConclusion
Setting up AutoGPT locally with Docker provides a robust, scalable, and maintainable solution for autonomous AI agent deployment. This containerized approach ensures consistency across different environments while providing the flexibility to customize and extend functionality as needed.
The combination of Docker’s isolation capabilities with AutoGPT’s autonomous features creates a powerful platform for exploring advanced AI applications. Whether you’re using it for research, development, or production purposes, this setup provides a solid foundation for leveraging autonomous AI capabilities.
Remember to regularly update your installation, monitor resource usage, and follow security best practices to ensure optimal performance and security of your AutoGPT deployment.
Additional Resources
- AutoGPT Official Documentation: https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
- Docker Documentation: https://docs.docker.com/
- OpenAI API Documentation: https://platform.openai.com/docs
- Docker Compose Reference: https://docs.docker.com/compose/
- Redis Documentation: https://redis.io/documentation